AGV vs. RGV vs. IGV: What's the Difference?
Release time:
2025-08-26
With the widespread rise of smart manufacturing globally, the subsequent Fourth Industrial Revolution has propelled rapid development in the smart manufacturing industry. As one of the core devices in intelligent logistics, mobile handling robots have experienced explosive growth in recent years.
Beyond common AGVs, RGVs and IGVs are also indispensable components within automated logistics systems.
I. Definitions of RGV, AGV, and IGV
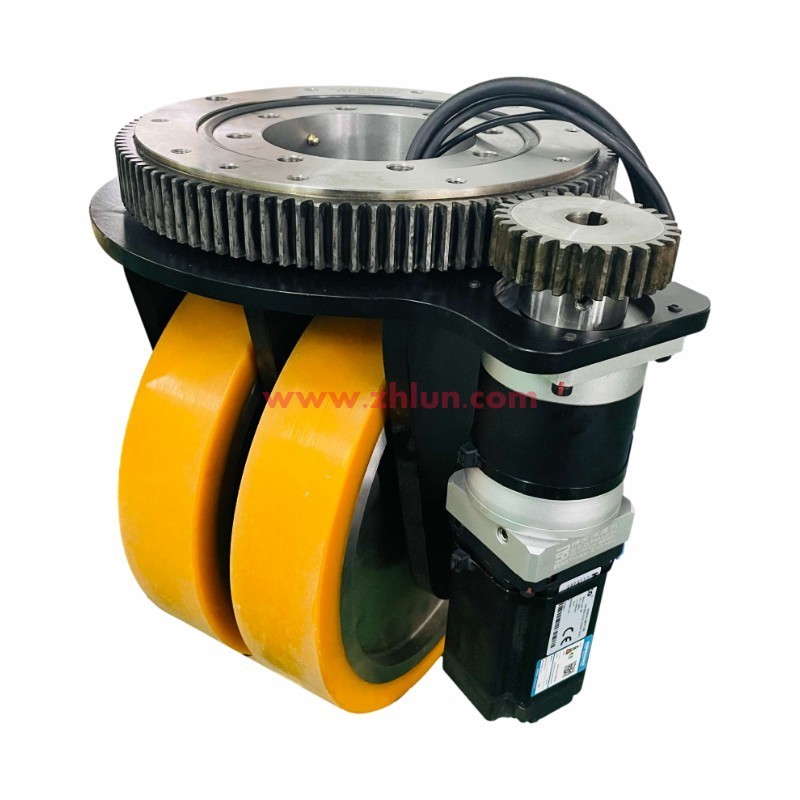
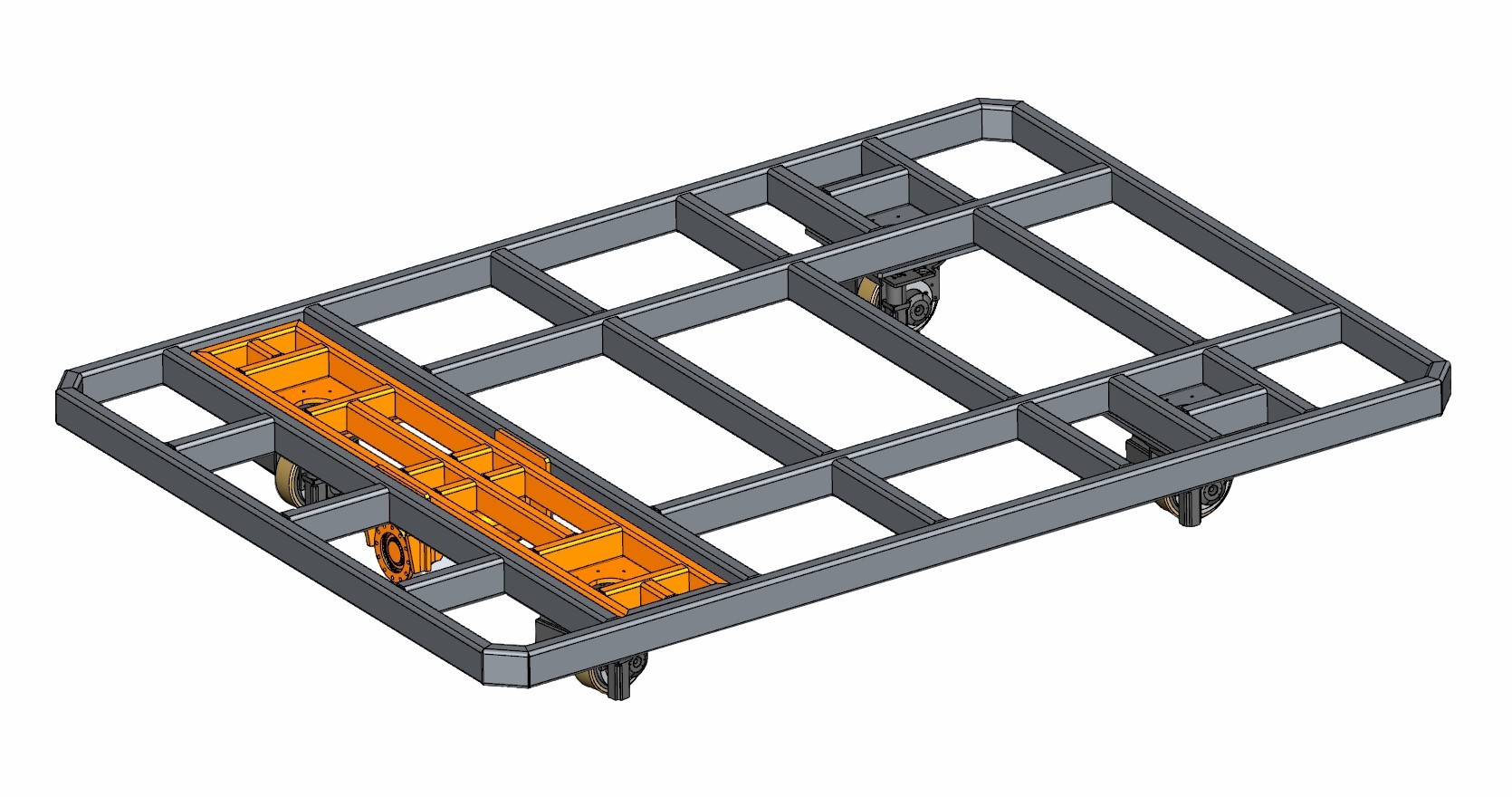
AGV: Automated Guided Vehicle. An AGV is a transport cart equipped with electromagnetic, optical, or other automatic guidance systems. It can travel along predetermined paths, featuring safety protection and various transfer functions.
RGV: Full name is Rail Guided Vehicle, also known as “Rail Shuttle Cart.” RGVs are commonly used in various high-density storage methods within automated warehouses. Cart aisles can be designed to any length as needed, and no other equipment needs to enter the aisle during cargo handling or movement. They offer high speed, high safety, and can effectively improve warehouse operational efficiency.
IGV: Stands for Intelligent Guided Vehicle. IGV is a new concept introduced in recent years. Compared to traditional AGVs, IGVs offer greater flexibility, requiring no fixed markers for navigation. Their routes are adaptable and can be dynamically adjusted based on actual production demands.
AGVs, RGVs, and IGVs do not replace one another based on varying levels of automation or intelligence. Instead, each plays an irreplaceable role in distinct application scenarios.
II. Characteristics and Application Scenarios of AGVs
AGVs (IGVs) are widely adopted in automated storage systems and flexible production lines, serving as the optimal choice for many manufacturing enterprises to enhance production efficiency and reduce costs. AGVs operate without fixed tracks, enabling broad applicability with diverse structural designs and control methods, resulting in numerous AGV types.
III. Key Advantages of AGVs
① High operational efficiency: AGVs feature automatic charging capabilities and can operate continuously 24/7 with safety redundancy, significantly boosting material handling efficiency.
② Labor savings: Fully digitalized AGVs effectively mitigate human error, elevating operational standards.
③ Superior flexibility and scalability: Intelligent AGVs employ advanced sensor fusion technology. Beyond traditional position, velocity, and acceleration sensors, they integrate machine vision, force feedback, and other multi-sensor systems for decision-making and control. Multi-sensor fusion configurations for associated equipment are already maturely implemented in existing AGV systems.
④ High reliability: Compared to inefficient manual handling and the unpredictable paths, speeds, and safety risks of forklifts and trailers, AGVs offer controllable travel routes and speeds with precise positioning and stopping. This significantly boosts material handling efficiency. Additionally, the AGV control center enables full-process monitoring of AGV carts, greatly enhancing reliability.
⑤ Superior Safety: AGVs feature comprehensive safety capabilities, including intelligent traffic routing, collision avoidance, multi-level warnings, emergency braking, and fault reporting. They excel in environments unsuitable for human workers.
Compared to RGVs, AGVs offer broader application scenarios. They play vital roles across various manufacturing processes—including machining, warehousing, and assembly—and have become one of the most iconic configurations in modern smart factories.


Related news
Products

Guangzhou Wisdom Wheel Science Technology Ltd.
No. 1436, Guangcong 9th Road, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
Whatsapp/MB: Kelly +86-18102686399
Jackson +8615012435018
Candy:+86 19396885135
CopyRight © 2024 Guangzhou Wisdom Wheel Science Technology Ltd.
Powered by www.300.cn SEO Tags En_CityProduct