Power, Precision, Performance: Selecting Your Perfect Drive Wheel.
Release time:
2025-08-21
Types Of Motor Drive Wheels
The AGV steering wheel is a core component of AGVs, directly determining their maneuverability, load capacity, and precision. So, what types are available to choose from? Let find out!
Vertical steering wheels and horizontal steering wheels are the two most fundamental structural classifications. Below, I will explain their types, advantages, and disadvantages in detail.
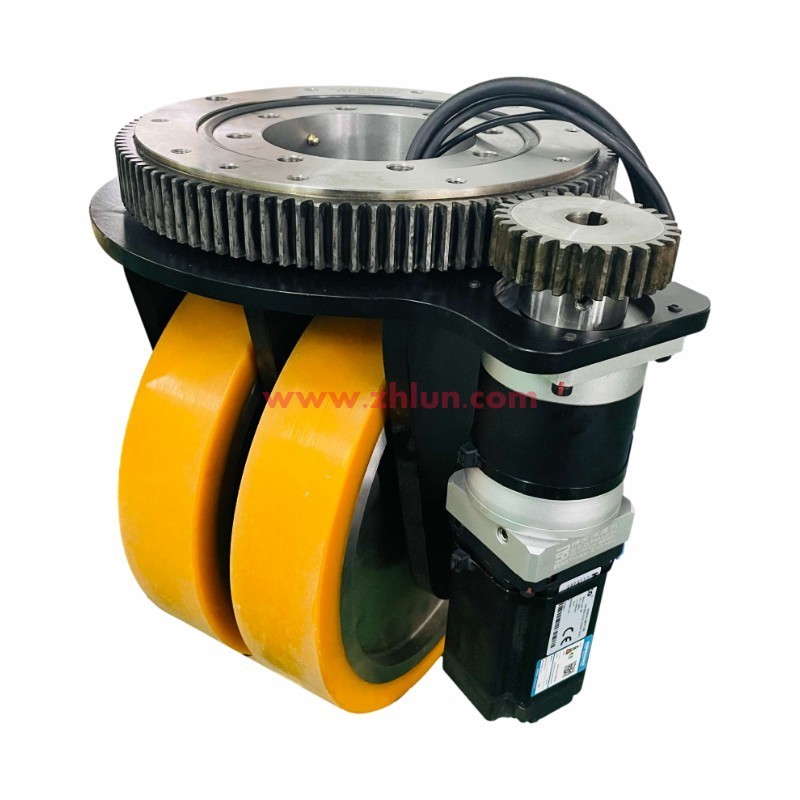
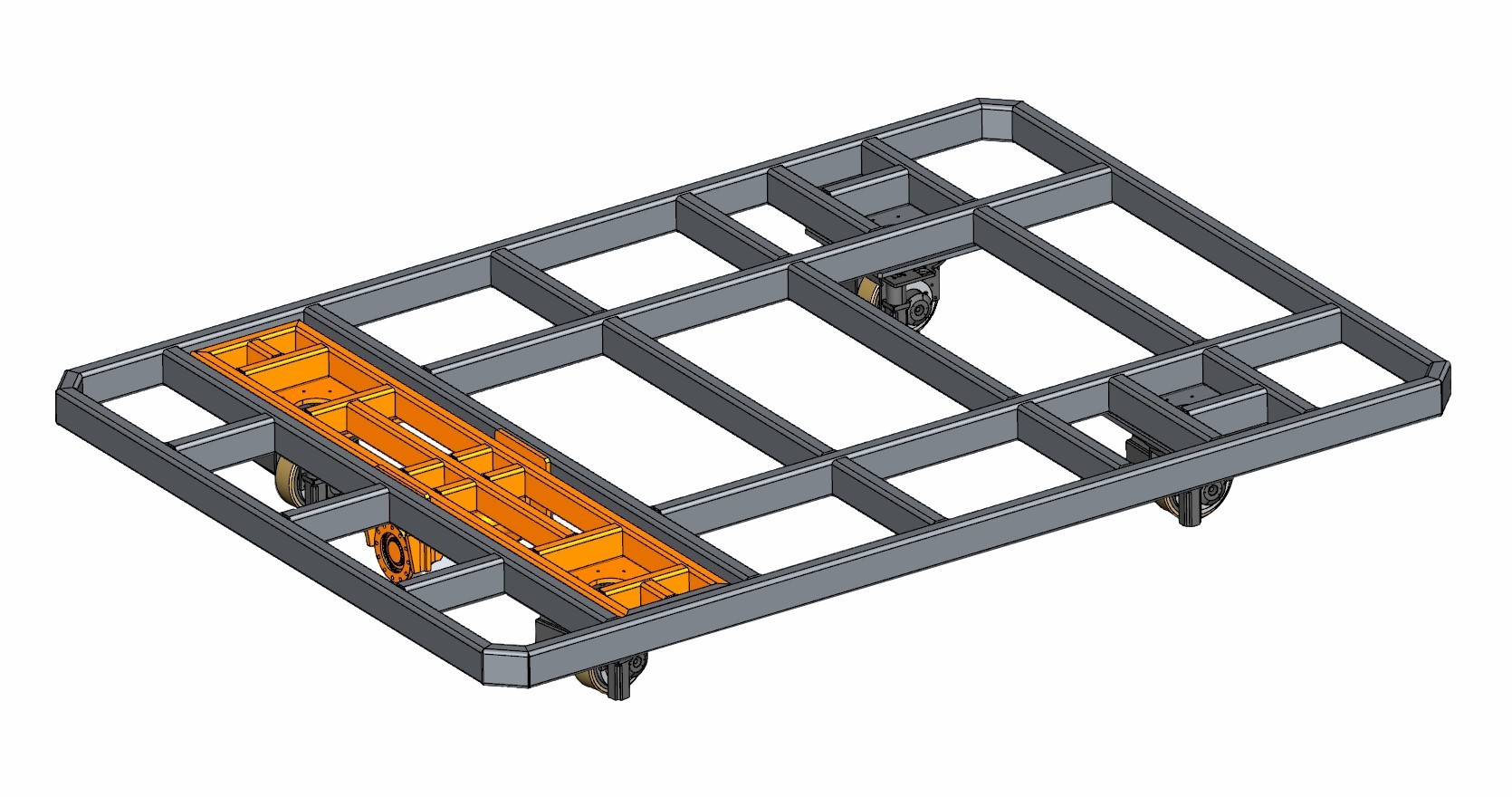
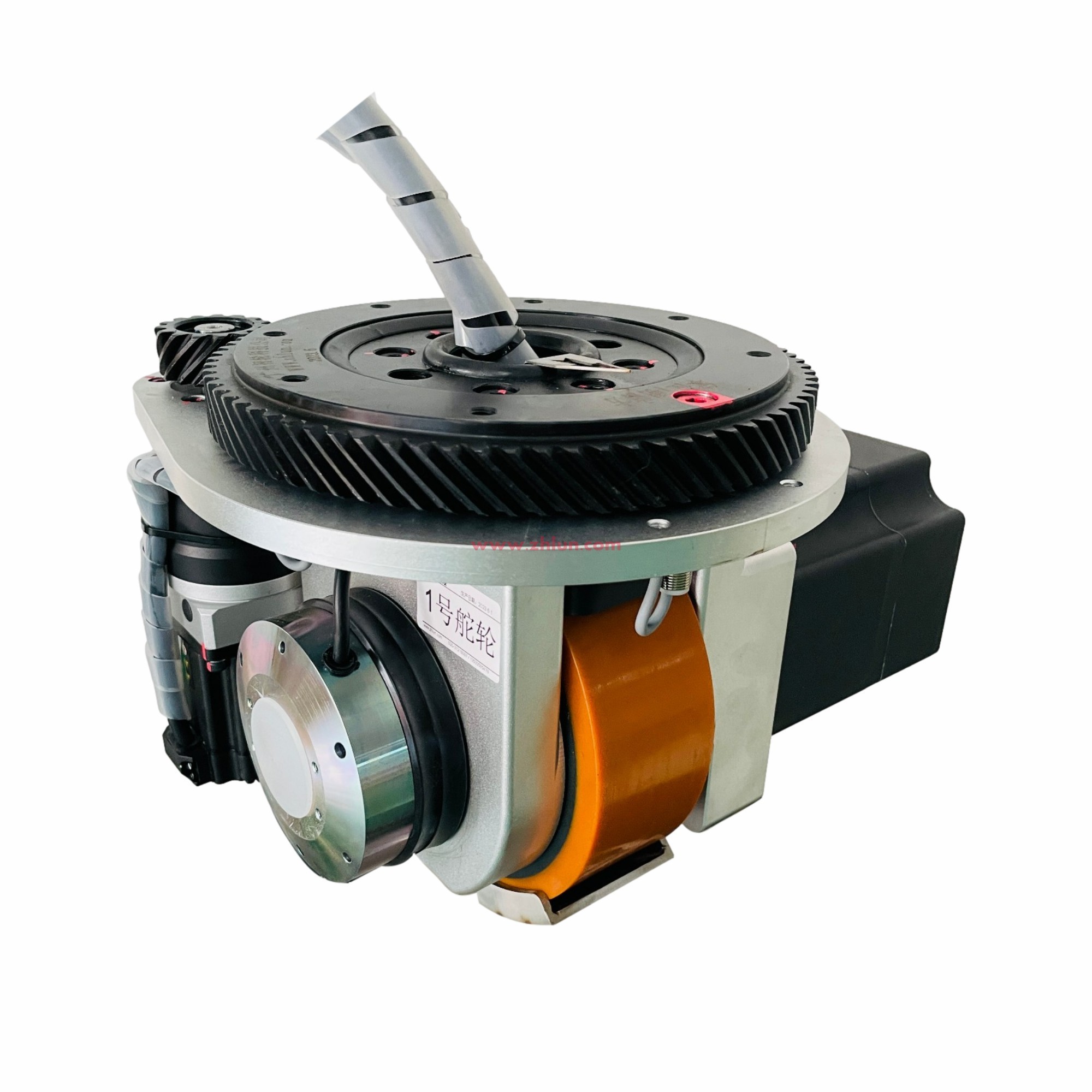
First, horizontal steering wheels have a lower height than vertical steering wheels. For example, the ZHLUN ZL-H130 series has a maximum load capacity of 800 kg per wheel, but an installation height of only 130 mm.
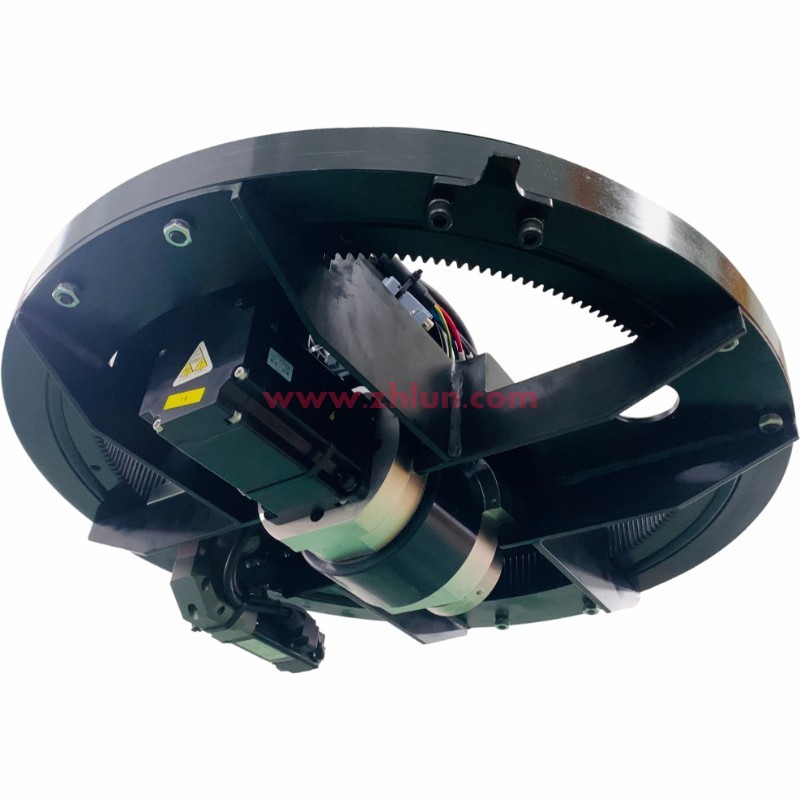

Structural diagram of the drive wheel: horizontally mounted on the AGV chassis. The motor, reducer, and other components are arranged parallel to the steering shaft. However, there are now ultra-short steering servo motor options available, which can reduce the overall rotational diameter of the drive wheel.
Advantages:
1. Low overall height, greatly saving AGV installation space and facilitating low-center-of-gravity, thin AGV design.
2. Neat appearance, with easier concealment and protection of wiring and components.
Disadvantages:
1. Complex structure, usually requiring more complex transmission designs (such as planetary reduction gears).
2. Relatively inconvenient maintenance, requiring the opening of covers or the removal of more components to access the core modules.
3. Heat dissipation challenges, as horizontal layouts may affect heat dissipation efficiency.

Applicable scenarios
Scenarios with strict restrictions on installation space and height. Examples include concealed/lift-type AGVs, box robots, and the bottom of composite robots.
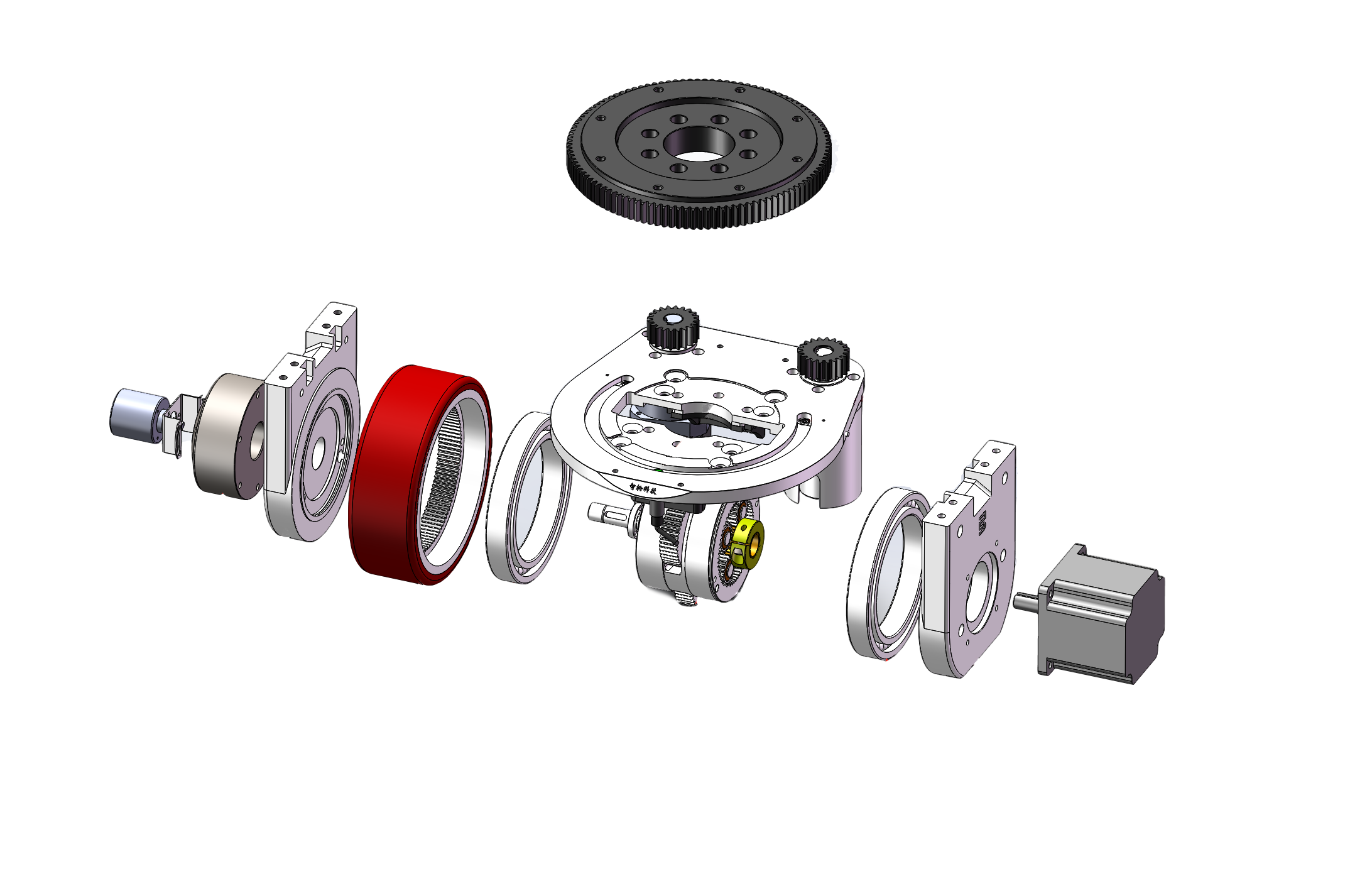
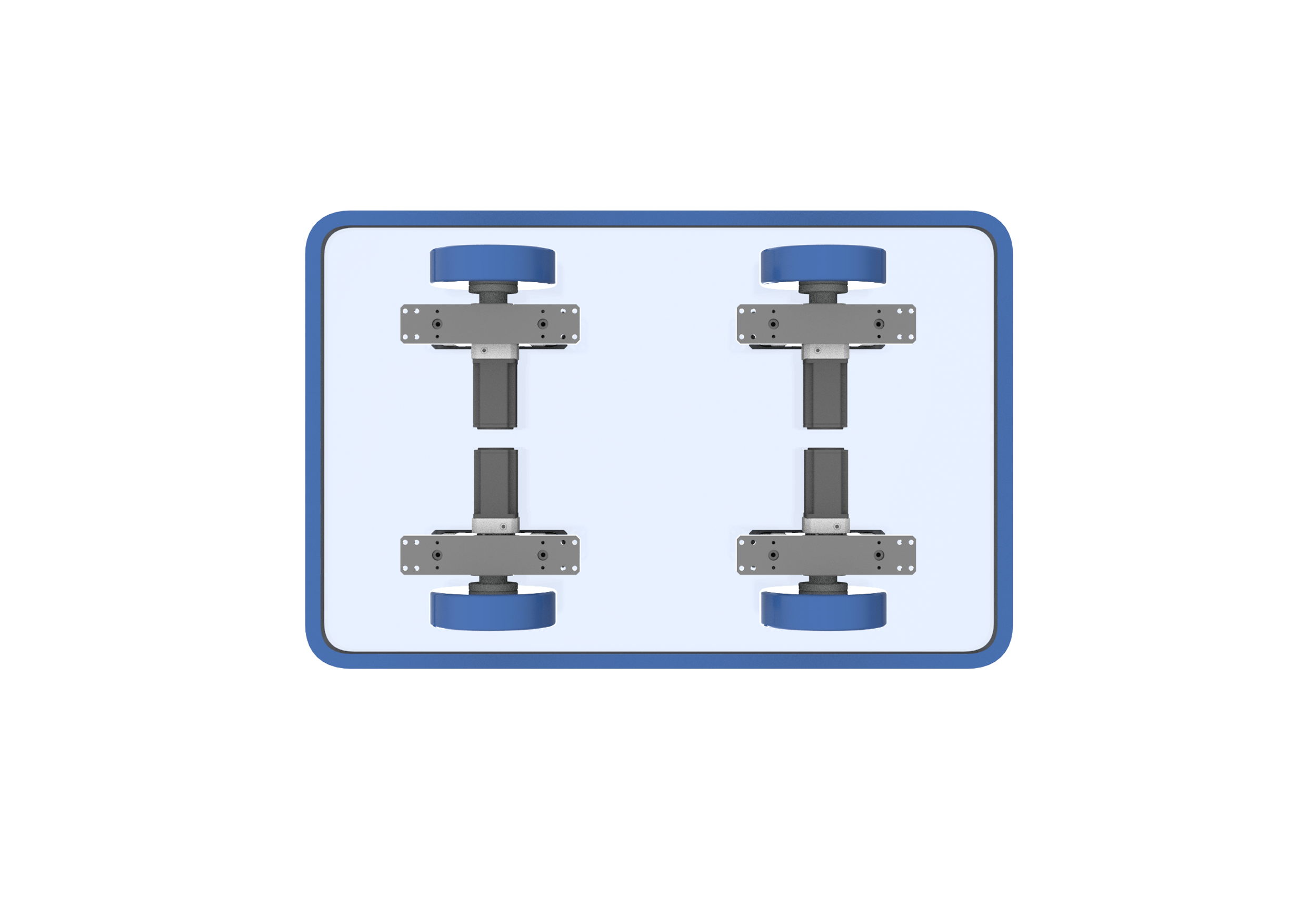
Secondly, the vertical steering wheel is installed vertically on the AGV body. The motor, reducer, etc. are arranged above and below the steering shaft.
Advantages:
1. Simple and stable structure with strong load-bearing capacity.
2. Easy maintenance, with key components (such as motors and encoders) easy to access and replace.
3. Good heat dissipation, with the motor placed vertically to facilitate natural convection heat dissipation.
Disadvantages:
1. The height is large, which occupies a lot of height space in the AGV body, resulting in a thicker overall AGV.
2. The center of gravity is high, which may affect the stability of the AGV during high-speed or sharp turns.
Applicable scenarios
Applications requiring high load capacity and ease of maintenance, but not high sensitivity to the overall height of the AGV, and narrow AGVs with limited drive wheel rotation diameter, such as traction AGVs and forklift AGVs.
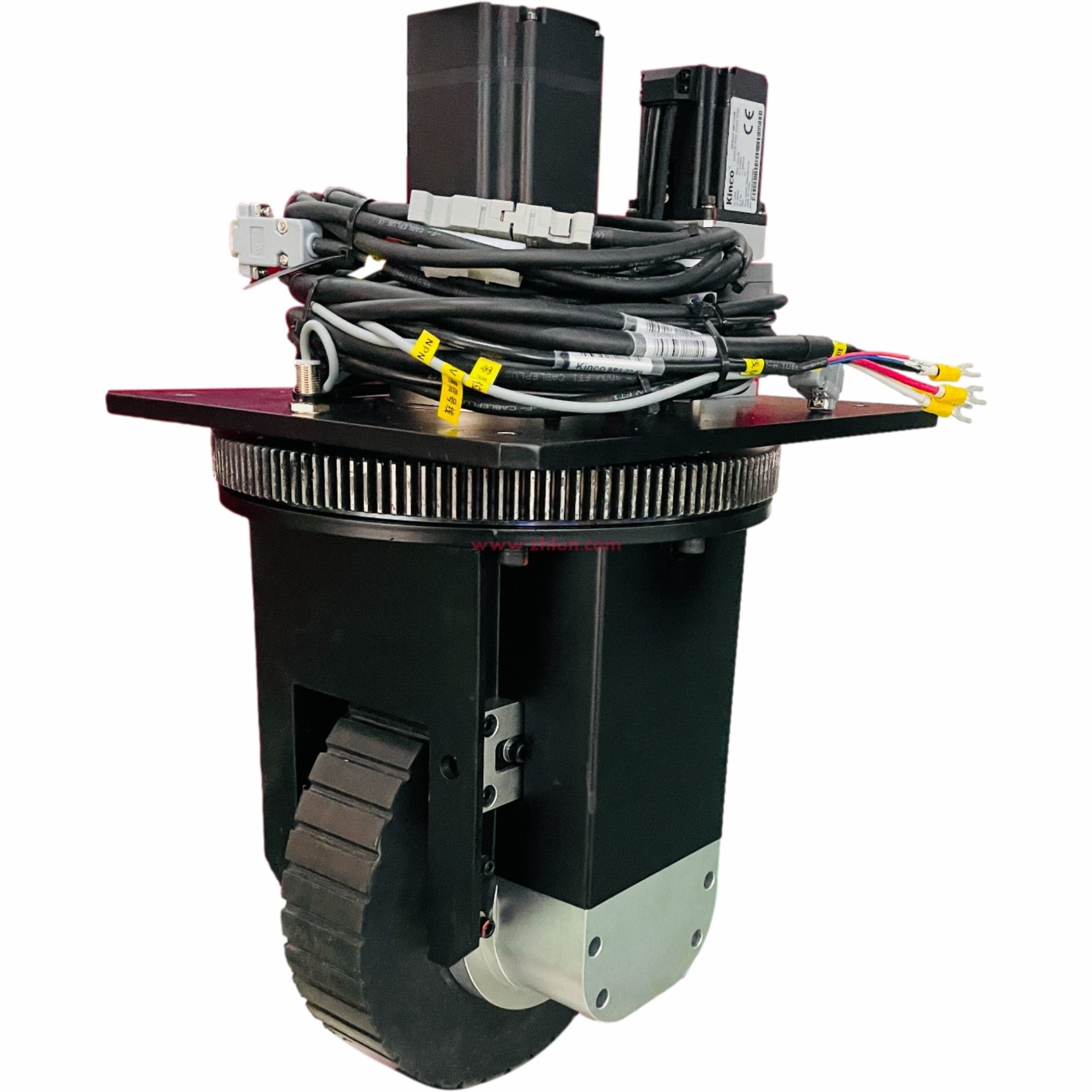

When choosing an AGV steering wheel type, consider the following factors:
Space & Layout:
Requires an ultra-thin, low-profile AGV (such as a stealthy AGV) → Horizontal steering wheels are preferred.
Sufficient space and load capacity are the top priority → Vertical steering wheels are a reliable and economical choice.
Mobility:
Simple, primarily straight paths → Differential wheels are sufficient.
Confined space, requiring on-the-spot turns or lateral movement → Dual steering wheels are the only option, offering unparalleled flexibility.
Precision & Stability:
Dual steering wheels, with feedback from two encoders, achieve extremely high travel and positioning accuracy.
Vertical steering wheels offer a more stable structure and perform better at high speeds and under heavy loads.

In short, there is no best steering wheel type, only the steering wheel type that best suits the specific application scenario. Modern AGV designs are often combinations and variations of these basic types to meet the increasingly complex needs of industrial logistics.
Related news
Products

Guangzhou Wisdom Wheel Science Technology Ltd.
No. 1436, Guangcong 9th Road, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
Whatsapp/MB: Kelly +86-18102686399
Jackson +8615012435018
Candy:+86 19396885135
CopyRight © 2024 Guangzhou Wisdom Wheel Science Technology Ltd.
Powered by www.300.cn SEO Tags En_CityProduct